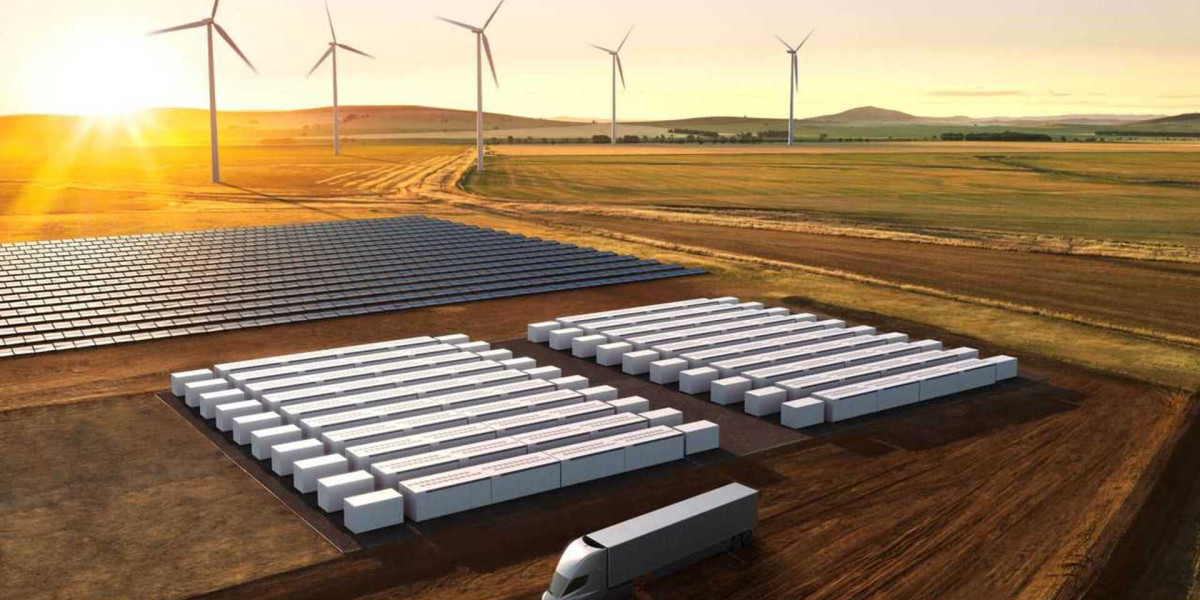
The stationary energy storage market is evolving rapidly as a critical component of the global shift toward renewable energy. Stationary energy storage systems (ESS) are increasingly seen as essential for balancing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like wind and solar, while also ensuring a stable and reliable energy grid. With the growing demand for clean energy and the need to enhance grid resilience, the stationary energy storage market is poised for significant growth in the coming years. These systems are not only pivotal for integrating renewable energy into the power grid but also for providing backup power, improving energy efficiency, and enhancing the overall performance of energy infrastructure. This article explores the dynamics of the stationary energy storage market, its key drivers, challenges, and future prospects.
Overview of the Stationary Energy Storage Market
Stationary energy storage systems are designed to store electricity for later use, offering a reliable solution for managing energy supply and demand. These systems are typically installed in fixed locations, such as utility grids, industrial facilities, or residential buildings, to store excess energy generated during low-demand periods. The stored energy can be discharged when demand peaks or when renewable energy generation is insufficient.
The global stationary energy storage market is growing rapidly, driven by several factors such as advancements in storage technologies, the need for grid modernization, and increasing investments in clean energy. Technologies such as lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and pumped hydro storage are revolutionizing the sector, offering more efficient and cost-effective storage solutions. As renewable energy adoption accelerates, the need for stationary energy storage will only continue to grow, creating a dynamic and fast-evolving market.
Market Size and Growth Forecast
The stationary energy storage market has witnessed impressive growth over the past few years and is expected to continue expanding at a robust pace. According to market reports, the global stationary energy storage market size is expected to exceed USD 60 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 20-25% during the forecast period. This growth is driven by increased demand for renewable energy integration, government incentives, and advancements in energy storage technology.
Among the different storage technologies, lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their efficiency, scalability, and decreasing costs. However, other energy storage technologies such as solid-state batteries, flow batteries, and pumped hydro storage are also gaining traction and are expected to play important roles in the evolving market.
Key Drivers of the Stationary Energy Storage Market
Several factors are driving the growth of the stationary energy storage market. These include the increasing adoption of renewable energy, the need for grid stability, advancements in storage technology, and supportive government policies.
1. Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
One of the key drivers of the stationary energy storage market is the need for efficient integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the electricity grid. These renewable sources are intermittent, meaning they do not always generate electricity when demand is high or when the sun isn't shining, or the wind isn't blowing. This intermittency creates challenges for grid operators in maintaining a consistent power supply.
Energy storage systems help mitigate these challenges by storing excess energy generated during periods of high renewable output and discharging it when generation is low or demand is high. By providing grid flexibility, stationary energy storage plays a crucial role in enabling the wider adoption of renewable energy and supporting the transition to a low-carbon energy grid.
2. Grid Modernization and Energy Resilience
Another significant driver for the growth of the stationary energy storage market is the ongoing modernization of power grids. Traditional energy grids were designed around centralized power plants that produce electricity and distribute it to consumers in a one-way flow. However, the rise of decentralized renewable energy generation, such as rooftop solar and distributed wind farms, has necessitated a shift toward more flexible, bidirectional grids capable of handling intermittent energy flows.
Stationary energy storage systems help modernize grids by enabling better management of energy distribution, improving grid reliability, and enhancing resilience in the face of disruptions, such as extreme weather events or power outages. This ability to provide backup power and stabilize the grid is essential as the world shifts to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources.
3. Technological Advancements in Energy Storage
Technological innovation in energy storage has been a key driver in the expansion of the stationary energy storage market. The development of more efficient, cost-effective, and scalable storage technologies is making stationary energy storage systems more accessible for various applications, from residential homes to large-scale utility projects.
Lithium-ion batteries, for example, have seen substantial reductions in cost and improvements in performance over the past decade. These advancements have made lithium-ion batteries the technology of choice for both residential and utility-scale energy storage. Other emerging technologies such as solid-state batteries, flow batteries, and compressed air energy storage are also gaining attention for their potential to offer even greater energy densities, longer lifespans, and lower costs.
4. Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a critical role in accelerating the adoption of stationary energy storage systems. Many governments worldwide have implemented supportive policies such as tax incentives, subsidies, and renewable energy targets to encourage the deployment of energy storage technologies.
For example, the U.S. has established several federal and state-level programs that provide financial support for energy storage projects, including tax credits and grants. Similarly, the European Union and countries like China and Japan have introduced renewable energy and energy storage mandates to drive growth in the sector. These policy frameworks are crucial in creating a favorable environment for investments in stationary energy storage infrastructure.
Segmentation of the Stationary Energy Storage Market
The stationary energy storage market can be segmented based on technology, application, and region. The key storage technologies include lithium-ion batteries, pumped hydro storage, flow batteries, and other emerging technologies.
1. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the most widely used energy storage technology due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and declining costs. Li-ion batteries are used in a wide range of applications, from residential energy storage systems to large-scale grid applications. The cost reduction of lithium-ion batteries over the past decade has made them the dominant technology in the stationary energy storage market.
2. Pumped Hydro Storage
Pumped hydro storage (PHS) is one of the oldest and most widely used large-scale energy storage technologies. It works by pumping water uphill to a reservoir during periods of low electricity demand and releasing it through turbines to generate electricity when demand is high. Although the technology is proven and efficient, it is geographically limited to regions with suitable topography and water resources.
Despite its limitations, pumped hydro storage remains a key player in the stationary energy storage market due to its ability to store large amounts of energy for extended periods.
3. Flow Batteries
Flow batteries are a promising energy storage technology that involves storing energy in electrolyte solutions, which flow through electrochemical cells to generate electricity. Flow batteries offer advantages such as long cycle life, high efficiency, and the ability to scale up for large applications.
While the technology is still in the development stage, flow batteries are expected to play a significant role in the stationary energy storage market as research and development progress and costs continue to decrease.
4. Other Emerging Technologies
Other energy storage technologies such as compressed air energy storage (CAES), thermal energy storage, and solid-state batteries are emerging as potential solutions for stationary energy storage. These technologies are still in the experimental or early commercial stages but hold promise for addressing the challenges of energy storage, such as cost, efficiency, and scalability.
Challenges Facing the Stationary Energy Storage Market
While the stationary energy storage market presents significant opportunities, several challenges must be addressed to realize its full potential.
1. High Capital Costs
One of the biggest challenges for the stationary energy storage market is the high upfront capital costs associated with energy storage systems. Although the cost of batteries and other storage technologies has declined significantly in recent years, the installation and integration of large-scale storage systems remain expensive. For many utilities and businesses, the high capital expenditure required for energy storage projects can be a significant barrier to adoption.
2. Energy Density and Storage Capacity
While storage technologies such as lithium-ion batteries offer high energy efficiency, they still face limitations in terms of energy density and capacity. Storing large amounts of energy requires large-scale storage systems, which can be expensive and require substantial space.
Emerging storage technologies like solid-state batteries and flow batteries offer potential solutions to these challenges, but they are still in the developmental phase and not yet commercially viable on a large scale.
3. Regulatory and Grid Integration Issues
Another challenge for the stationary energy storage market is the complex regulatory landscape and the need for grid integration. Many countries and regions have different regulations governing the deployment of energy storage systems, which can create barriers for market entry. In addition, integrating stationary energy storage systems into existing grids can be complex and requires careful planning to ensure that the storage infrastructure complements grid operations.
4. Lifecycle and Sustainability
The environmental impact and sustainability of energy storage technologies are also areas of concern. The production of batteries and other storage technologies requires raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can have significant environmental and ethical implications. Additionally, the recycling and disposal of batteries at the end of their lifecycle need to be addressed to reduce the environmental footprint of stationary energy storage systems.
Future Outlook of the Stationary Energy Storage Market
The future of the stationary energy storage market looks promising, with continued growth expected in the coming years. As renewable energy adoption increases and grid modernization efforts accelerate, the demand for energy storage systems will continue to rise. Technological advancements will also play a significant role in driving down costs, improving efficiency, and expanding the potential applications of energy storage systems.
Emerging technologies such as flow batteries, solid-state batteries, and compressed air energy storage are expected to enhance the capabilities of stationary energy storage systems, enabling more scalable, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions. As these technologies mature, they could reshape the market and create new opportunities for innovation and investment.
Conclusion
The stationary energy storage market is a critical component of the transition to a more sustainable, low-carbon energy future. With the integration of renewable energy sources and the need for grid stability, energy storage systems play a vital role in enhancing energy security, improving grid resilience, and enabling a cleaner energy mix. While challenges remain, technological advancements, supportive government policies, and increasing demand for renewable energy will drive the growth of the stationary energy storage market in the years to come. As the market evolves, stationary energy storage will continue to be a key enabler of global sustainability efforts and the future of energy infrastructure.
More Trending Reports